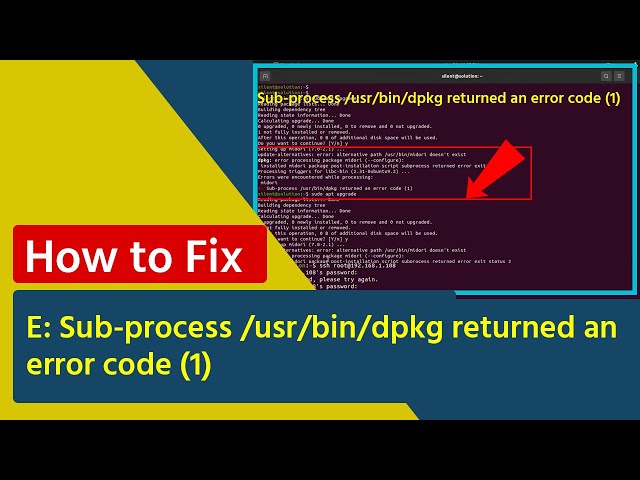
Have you ever tried to install or update a package on your Linux system, only to be stopped by the frustrating message: “Dpkg returned an error code 1”? If you’re facing this problem, you’re not alone—and it can feel like your system is suddenly stuck in a loop of errors.
But don’t worry, this issue isn’t as complex as it seems. You’ll discover simple, step-by-step solutions to fix this error quickly. By the end, you’ll have your system running smoothly again, without the stress and confusion. Ready to take control and solve this problem once and for all?
Let’s dive in.
Credit: www.youtube.com
Common Causes Of Dpkg Error Code 1
Dpkg error code 1 usually happens because of broken packages or dependency issues. Sometimes, the package files are corrupted or incomplete. This stops the installation or removal process.
Another common cause is lack of disk space. If the system runs out of space, dpkg cannot complete tasks. Also, conflicting packages can block each other.
Permissions problems may cause the error too. If dpkg does not have the right access, it will fail. Using commands like sudo can help fix this.
| Cause | Description |
|---|---|
| Broken packages | Packages that are damaged or incomplete. |
| Dependency issues | Missing or conflicting required packages. |
| Low disk space | Not enough storage for installation. |
| Permission errors | Insufficient user rights for dpkg. |

Credit: www.youtube.com
Checking For Broken Dependencies
Broken dependencies often cause the dpkg error code 1. To check for these issues, run sudo apt-get check. This command scans for missing or broken packages. Fixing broken packages helps the system work correctly.
Use sudo apt-get install -f to fix broken dependencies automatically. It tries to fix and complete package installation. This step often resolves dpkg errors caused by dependency problems.
Another useful command is dpkg --configure -a. It configures any unpacked but unconfigured packages. Running this can clear stuck installations and fix errors.
| Command | Purpose |
|---|---|
sudo apt-get check | Check for broken dependencies |
sudo apt-get install -f | Fix broken packages automatically |
dpkg --configure -a | Configure unpacked packages |
Cleaning Up Package Database
Cleaning the package database helps fix the dpkg error code 1. Start by running sudo dpkg --configure -a. This command tries to fix unfinished installs.
Next, use sudo apt-get install -f. It fixes broken dependencies automatically. Sometimes, removing lock files helps. Use sudo rm /var/lib/dpkg/lock-frontend and sudo rm /var/lib/dpkg/lock.
Clear the package cache with sudo apt-get clean. This frees up space and removes old files. Then, try updating package lists with sudo apt-get update. This makes sure you have the latest info.
If the problem stays, check the status of packages. Use dpkg -l | grep ^..r to find broken packages. Remove or reinstall them carefully.
Reconfiguring Packages
Reconfiguring packages fixes many dpkg error code 1 problems. Start by running sudo dpkg --configure -a. This command tries to finish installing packages. Sometimes, broken packages cause errors. This command helps fix those broken parts.
If the error stays, check the package causing trouble. Use dpkg -l | grep -v ^ii to see packages not fully installed. Then, try removing or reinstalling that package. Commands like sudo apt-get install -f fix missing dependencies.
Clean package cache too. Run sudo apt-get clean to remove old files. This frees space and can help fix issues.
Patience is key. Some fixes need repeating commands. Errors often come from interrupted installs or network problems.
Using Force Options Safely
Using force options with dpkg can fix some errors but needs care. These options override warnings and ignore dependencies. This can cause problems if used wrongly. Always check which packages are causing issues first. Run sudo dpkg --configure -a to fix broken installs before using force.
Common force options include:
| Option | What it does |
|---|---|
| –force-overwrite | Allows overwriting files from other packages |
| –force-depends | Ignores dependency problems |
| –force-remove-reinstreq | Forces removal of packages needing reinstallation |
Use these options only if you understand the risks. Backup important data first. Test commands on non-critical systems if possible. Always try safer fixes before forcing dpkg actions.
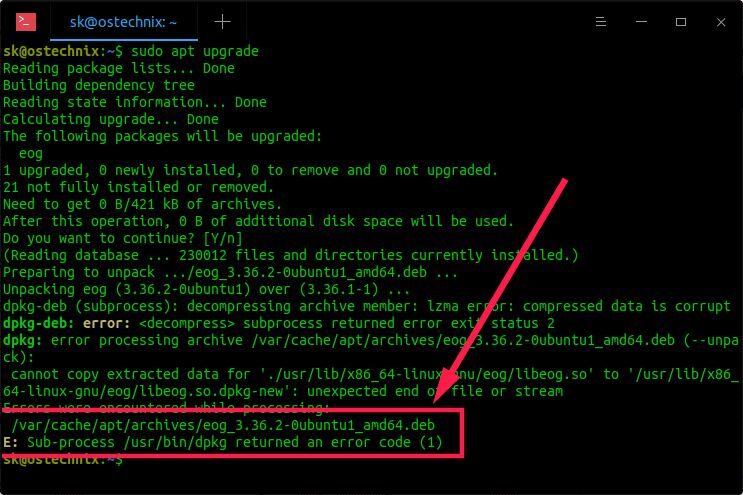
Credit: ostechnix.com
Frequently Asked Questions
What Causes Dpkg Returned An Error Code 1?
It usually means a package installation or removal failed due to broken files or conflicts.
How Can I Fix Dpkg Error Code 1 Quickly?
Run sudo dpkg –configure -a to fix broken packages and resolve installation issues.
Does Dpkg Error Code 1 Affect System Updates?
Yes, it can stop updates until the package errors are fixed properly.
Can Insufficient Disk Space Cause Dpkg Error Code 1?
Yes, low disk space can prevent package installation, triggering this error code.
Conclusion
Dpkg error code 1 can stop your installation quickly. Fixing broken packages helps solve this issue fast. Always check your system for missing files or locks. Running simple commands often clears the problem. Keep your software updated to avoid future errors.
Troubleshooting step by step makes the process easier. Don’t let this error block your work. Stay patient and follow the solutions carefully. This way, your system will run smoothly again.

